Posted on 09 May 2011. Tags: adults ages, amount of money, avastin, grunwald, journal of medicine, loss of vision, new england journal of medicine, retina, study authors, visual impairment
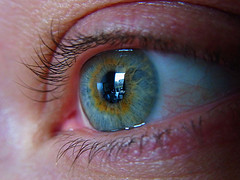 Based on the results of a recent study in the United States, Avastin is equally effective against macular degeneration to Lucentis. Avastin is an anti-cancer drug while Lucentis is the leading drug for macular degeneration; Avastis, however, is 40 times cheaper than Lucentis.
Based on the results of a recent study in the United States, Avastin is equally effective against macular degeneration to Lucentis. Avastin is an anti-cancer drug while Lucentis is the leading drug for macular degeneration; Avastis, however, is 40 times cheaper than Lucentis.
The study basically compared Avastin to Lucentis. Both drugs were developed by Genentech, a US firm owned by the Swiss laboratory Roche.
While the test was still ongoing, the researchers randomly assigned a total of 1,208 people with neovascular macular degeneration to get Avastis or Lucentis injections in the eye on a regular basis. That is either done monthly or on an as needed basis, depending on the patients’ monthly evaluation.
Macular degeneration is a condition that usually affects older adults and results in a loss of vision around the center of the visual field due to damage to the retina. It is the most common cause of visual impairment among adults ages 50 and above. This condition will make it almost impossible for the patient to recognize faces, let alone read. However, they usually have enough peripheral vision to allow them to carry on regular daily activities.
After a year of trials, Avastis and Lucentis have the same effects on the respondents’ visual acuity when they are administered following the same schedule. However, the cost of treatment varies widely said Doctor Juan Grunwald, one of the study authors.
The average cost per patient of those who were administered with Lucentis is $23,400. That is a very huge amount of money compared to the $385 cost per patient treated with Avastis.
This study appears in the most recent issue of The New England Journal of Medicine.
Posted in Health
Posted on 24 November 2010. Tags: david ludwig, european researchers, food restrictions, high glycemic index, journal of medicine, new england journal, protein group, refined carbs, weight maintenance, western european countries
 Weight-loss gurus may have claimed that increased protein and less refined carbohydrates in the diet can keep a person from gaining weight. However, a team of European researchers confirmed this claim based on the study they have compiled with a number of men, women and their families.
Weight-loss gurus may have claimed that increased protein and less refined carbohydrates in the diet can keep a person from gaining weight. However, a team of European researchers confirmed this claim based on the study they have compiled with a number of men, women and their families.
The study, which was published in the New England Journal of Medicine, was conducted by Dr. Thomas Meinert Larsen of the University of Copenhagen and his colleagues. Initially, they had 773 men and women with their families from eight western European countries enrolled in the study.
Each family was arbitrarily assigned with one weight-maintenance diet out of five categories for 26 weeks. One group served as the control with no food restrictions. The rest were assigned various proportions of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates that were categorized as high or low glycemic index, which measures how rapid a food is converted to sugar in the blood.
Some people dropped out of the study, which consist mostly of the group from high protein or low-glycemic index category, as well as the low-protein and high-glycemic group.
548 people completed the study, and among them, only those who consumed a low-protein and high-GI diet gained a remarkable amount of weight.
Meanwhile, the researchers discovered that those people who were included in the high-protein gained one kilogram less than those who were included in the low-protein group. The same happened with the low-glycemic index versus high-glycemic index diet.
Based on the study, among the participants who had lost a minimum of eight percent body weight while on a low-calorie diet, those who followed a maintenance diet high in protein and low in refined carbs for the next six months are the least possible to regain any weight. They were also the least likely to drop out of the study.
According to Dr. David Ludwig, anyone can lessen their calorie intake and lose weight for a short span of time; however, the difficult part is to keep it off. However, he suggests for the people to try this diet at home.
Posted in Health
 Based on the results of a recent study in the United States, Avastin is equally effective against macular degeneration to Lucentis. Avastin is an anti-cancer drug while Lucentis is the leading drug for macular degeneration; Avastis, however, is 40 times cheaper than Lucentis.
Based on the results of a recent study in the United States, Avastin is equally effective against macular degeneration to Lucentis. Avastin is an anti-cancer drug while Lucentis is the leading drug for macular degeneration; Avastis, however, is 40 times cheaper than Lucentis.
 Weight-loss gurus may have claimed that increased protein and less refined carbohydrates in the diet can keep a person from gaining weight. However, a team of European researchers confirmed this claim based on the study they have compiled with a number of men, women and their families.
Weight-loss gurus may have claimed that increased protein and less refined carbohydrates in the diet can keep a person from gaining weight. However, a team of European researchers confirmed this claim based on the study they have compiled with a number of men, women and their families.